Y Combinator graduate OpenPhone is raising a $2 million funding round led by Slow Ventures. The company is working on an app that lets you seamlessly get a business phone number without a second phone or a second SIM card.
Y Combinator, Kindred Ventures, Garage Capital, 122WEST Ventures and others are also participating in today’s funding round.
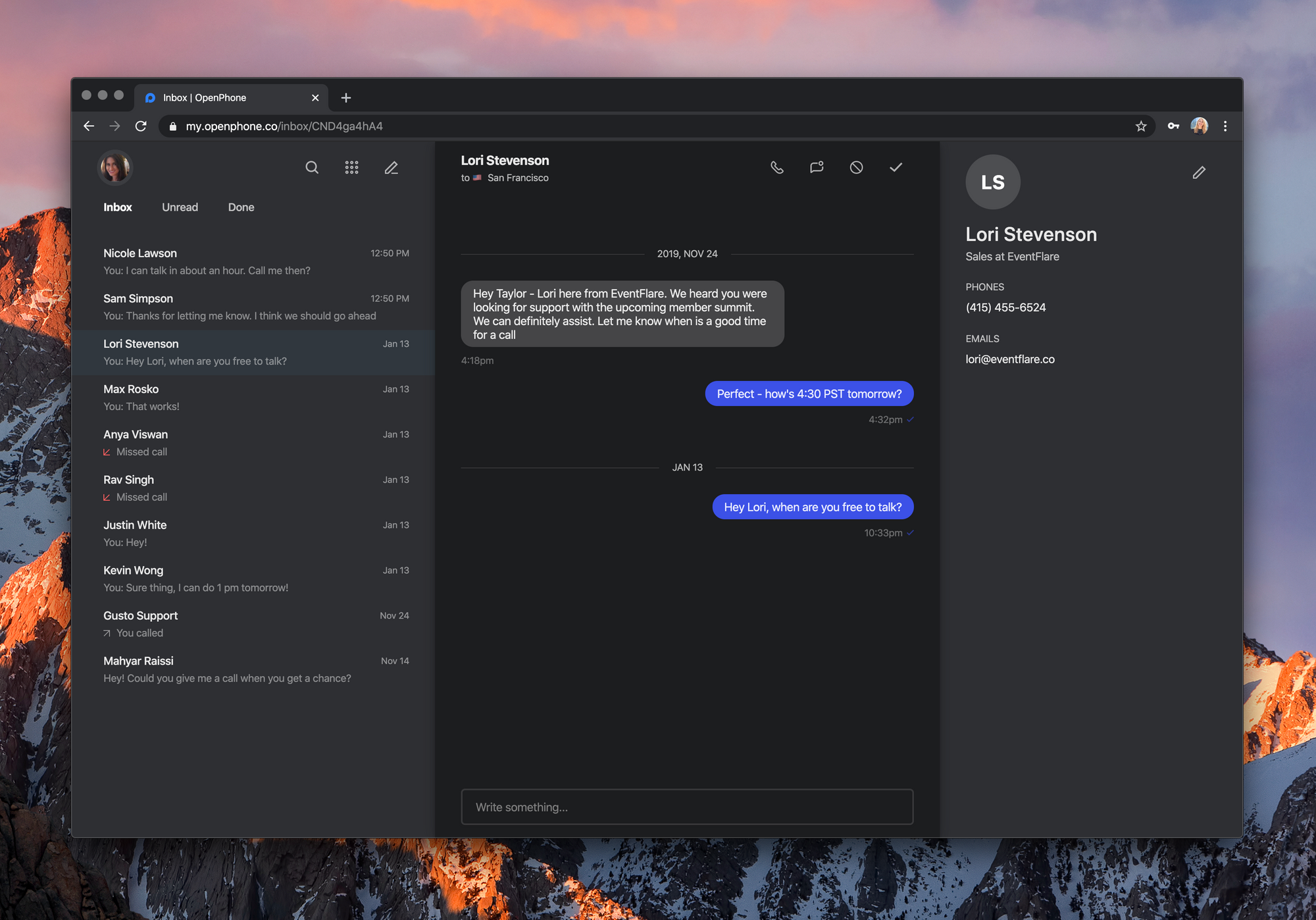
Compared to Aircall and other enterprise solutions, OpenPhone targets small and medium companies who want a mobile-first, easy-to-use solution to take advantage of a second phone number.
For instance, if you’re a freelancer and you hate handing out your personal phone number, OpenPhone lets you separate your personal and professional life more easily.
OpenPhone works on iPhone, iPad and Android. You can also use a web interface to interact with the app from your computer. It currently costs $10 per month per user. For that price, you get a local number, a toll-free number or you can port an existing phone number. 5,000 people are using OpenPhone right now.
You can then use that number for unlimited calls and texts in the U.S. and Canada. Behind the scene, OpenPhone uses your internet connection to establish voice-over-IP calls.
The startup has been working on collaborative features so that you can use OpenPhone with multiple users. For instance, you can share a phone number with other users so that your team can answer text messages faster and pick up the phone more often. The company has also launched a Slack integration that lets you receive a notification when somebody calls or texts your phone number.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/37N74YJ
Comments
Post a Comment