A 9-year-old is smashing the shuttle far and wide, and frantically pacing back and forth on the court in Bangalore, India, as her competition refuses to back down. Her rival is not a human. She is playing against a machine that is mimicking the game of badminton legend P.V. Sindhu, toned down a few notches to adjust for the age difference.
By the court, her father, Jayanth Kolla, is watching the game and taking notes. Kolla is a familiar name in the tech startup and business ecosystem in India. For the last eight years, he has been helming the research firm Convergence Catalyst, which covers mobility, telecom, AI and IoT.
When his daughter showed interest in badminton, Kolla rushed to explore options, only to realize that the centuries old sports could use some deep tech.
He reached out to a few friends to explore if they could build a device. “I have always wondered how a younger version of players who have made it to the professional arena must have played like,” he said in an interview.
Months later, they had something better.
Sensate Technologies
Kolla founded Sensate Technologies last year and has hired many industry experts and data scientists from Stanford, MIT, and India’s IIT. Sensate is building solutions on deep technologies such as AI, ML, advanced analytics, IoT, robotics and blockchain.
In the last year, the bootstrapped startup has developed seven prototypes, five of which are for sports. It holds eight patents. Which brings us back to the court.
One of the prototypes that Sensate has built is the machine that Kolla’s daughter is playing against. In a recent interview, he demonstrated how Sensate was able to accurately map how a player moves on the court and goes about smashing the shuttle by just looking at two-dimensional videos on YouTube and mobile camera feed. This has been built using Computer Vision AI.
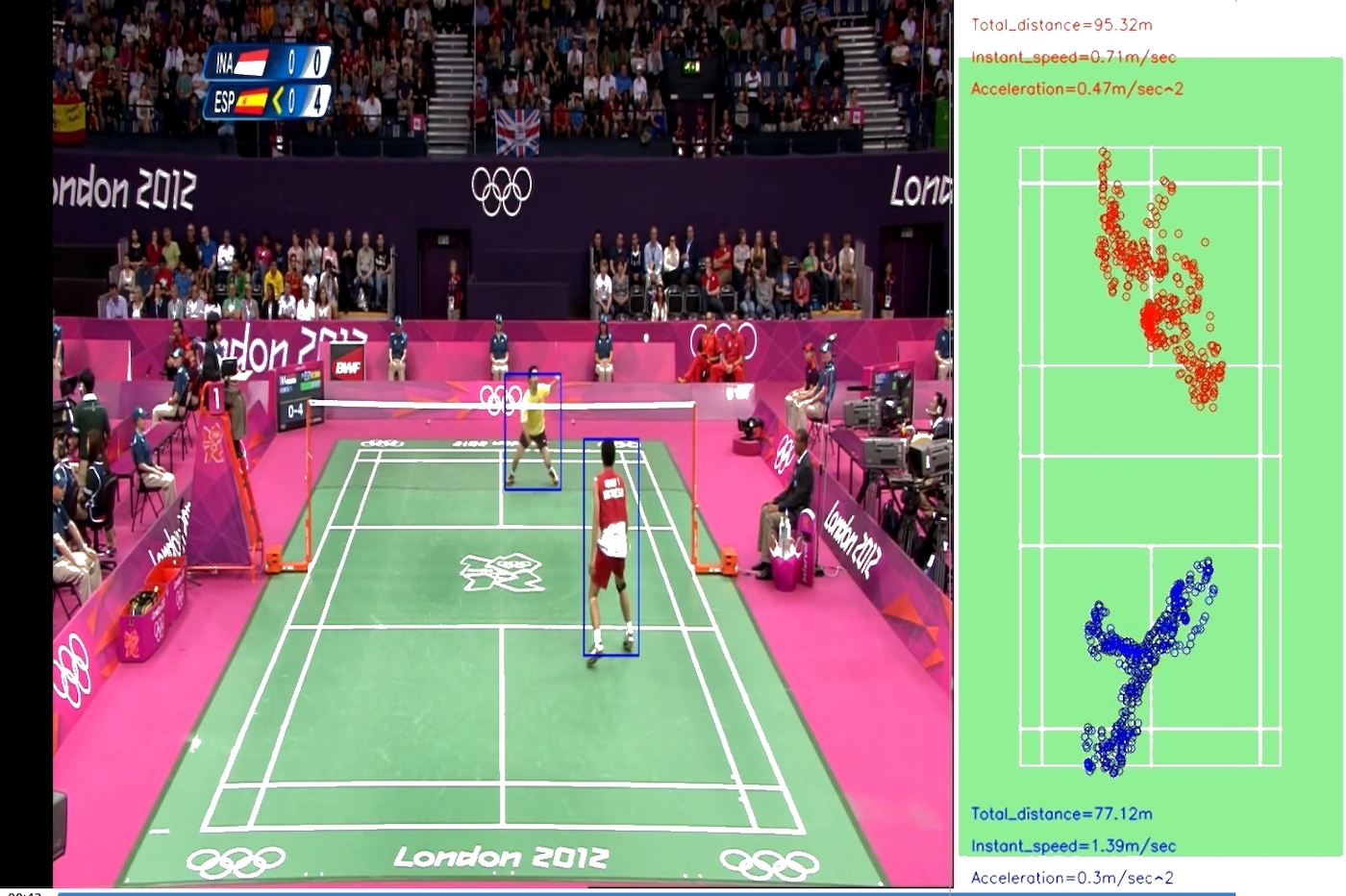
It then fine tunes the gameplay in accordance with the age difference, which is input into a machine that can now mimic that player to a great level, said Kolla.
A handful of startups and established players have sought to address the sports tech market in recent years. SeeHow, another India-based startup, builds and embeds sensors in bats and balls to track specific types of data that batsmen and bowlers generate.
Kolla’s aim is to turn Sensate Technologies into a global deep tech venture foundry and build 20 odd products that would then branch into multiple companies operating in 11 different industries.
Microsoft last year partnered with Indian cricket legend Anil Kumble’s company Spektacom to work on a number of solutions including a smart sticker for bats that contains sensor tech designed to track the performance.
But Kolla’s ambitions go way beyond sports tech.
“The best part about deep technology solutions and platforms is that you build solutions on these technologies to solve a problem in a particular sector and with very little incremental effort, they can solve problems in a completely different sector,” he said.
Kolla, a former product manager at Motorola and Nokia, among other companies, said the startup is also in discussion with one of the world’s biggest companies that is looking to license its tech for their healthcare stack. “This validates our approach.” He declined to name any potential clients as the talks have not materialized yet.
from TechCrunch https://ift.tt/32DjwZg
Comments
Post a Comment